Table of contents
Introduction 👓
Cloud has become an integral part of modern life, revolutionizing the way we store, access, and share data. Cloud computing has transformed the way we work, communicate, and build things.
First of all, there is nothing like a "Cloud" that powers the Internet. It is somebody else's computer in a Datacenter.
So let's get started on this journey of Cloud Computing.🚂

Definitions of Cloud Computing 📝
#1 Cloud computing refers to the delivery of on-demand computing resources, such as servers, storage, applications, and services, over the internet. Basically, the servers that are accessed over the Internet, and the software and databases that run on those servers. These servers are located all over the world.
#2 Cloud computing abstracts computation, storage, and network infrastructure assembled as a platform on which applications and systems can be deployed quickly.
#3 Massive scalable IT-related capabilities are provided as a "service" using the internet to multiple customers.
What is Infrastructure? 🏭
Infrastructure means the physical and virtual components that support an organization's IT systems and processes. It includes the hardware, software, networks, and facilities necessary for an organization to operate and communicate.
Examples of physical infrastructure include Hardware, Networks, and Data servers.
Software infrastructure includes operating systems, middleware, databases, and applications.
Virtual infrastructure refers to the use of virtualization technologies such as VMWare or Virtual box etc. to create multiple virtual instances of operating systems or applications on a single physical machine. This can help organizations optimize their hardware utilization, improve their application deployment speed, and simplify their IT management.
What do businesses worry about when it comes to Infrastructure? 👻

Every business has some concerns or things to worry about but in most cases, the following are the main ones:
Service Availability (24*7)
Maintaining the service
Unpredictable growth of users (from 100 to 100Million or more)
Data center management (management is essential to ensure that the IT infrastructure is running smoothly and securely)
Elasticity (easily scale up or down its computing resources in response to changing demand)
Redundancy
Infrastructure Refresh
Security
Why Cloud is better than Classical Enterprise Infrastructure? 🌧
Turns Capital Expenditure into Operational Expenditure. (CapEx is typically a one-time, up-front expenditure to purchase or secure tangible resources, OpEx is spending money on services or products over time. Renting a convention center, leasing a company vehicle, or signing up for cloud services are all examples of OpEx)
Businesses can quickly and easily scale their computing resources up or down as needed to meet changes in demand.
In this image, you can see how the "classical model" fails in terms of elasticity.


Cloud providers invest heavily in the reliability and availability of their infrastructure, which means businesses can benefit from a high level of uptime and availability for their IT systems.
In terms of Security and Confidentiality, Cloud offers a high level of security for its infrastructure and the data stored within it. This can help businesses ensure the security and confidentiality of their data.
Classical vs. Cloud scaling model 📦


Services provided by Cloud 🌤
These days cloud is providing a lot of services but the main ones are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Other services are just a subset of IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.

IaaS 🏭
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service, which is a cloud computing service model that provides users with an Infrastructure to use (virtualized computing, hardware, servers and storage as a service on the internet).
In an IaaS model, the cloud provider is responsible for maintaining the hardware, network connectivity (to the internet), and physical security. You’re responsible for everything else: operating system installation, configuration, and maintenance; network configuration; database and storage configuration; and so on. With IaaS, you’re essentially renting the hardware in a cloud data center, but what you do with that hardware is up to you.
Examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and DigitalOcean.
PaaS 🍽
Platform as a Service provides sets of services and workflows that specifically target developers, who can use shared tools, processes, and APIs to accelerate the development, testing, and deployment of applications. PaaS provides a Runtime environment, Operating system and Middleware as well.
Examples of PaaS providers include Heroku, Google Cloud, AWS, AppFog etc.
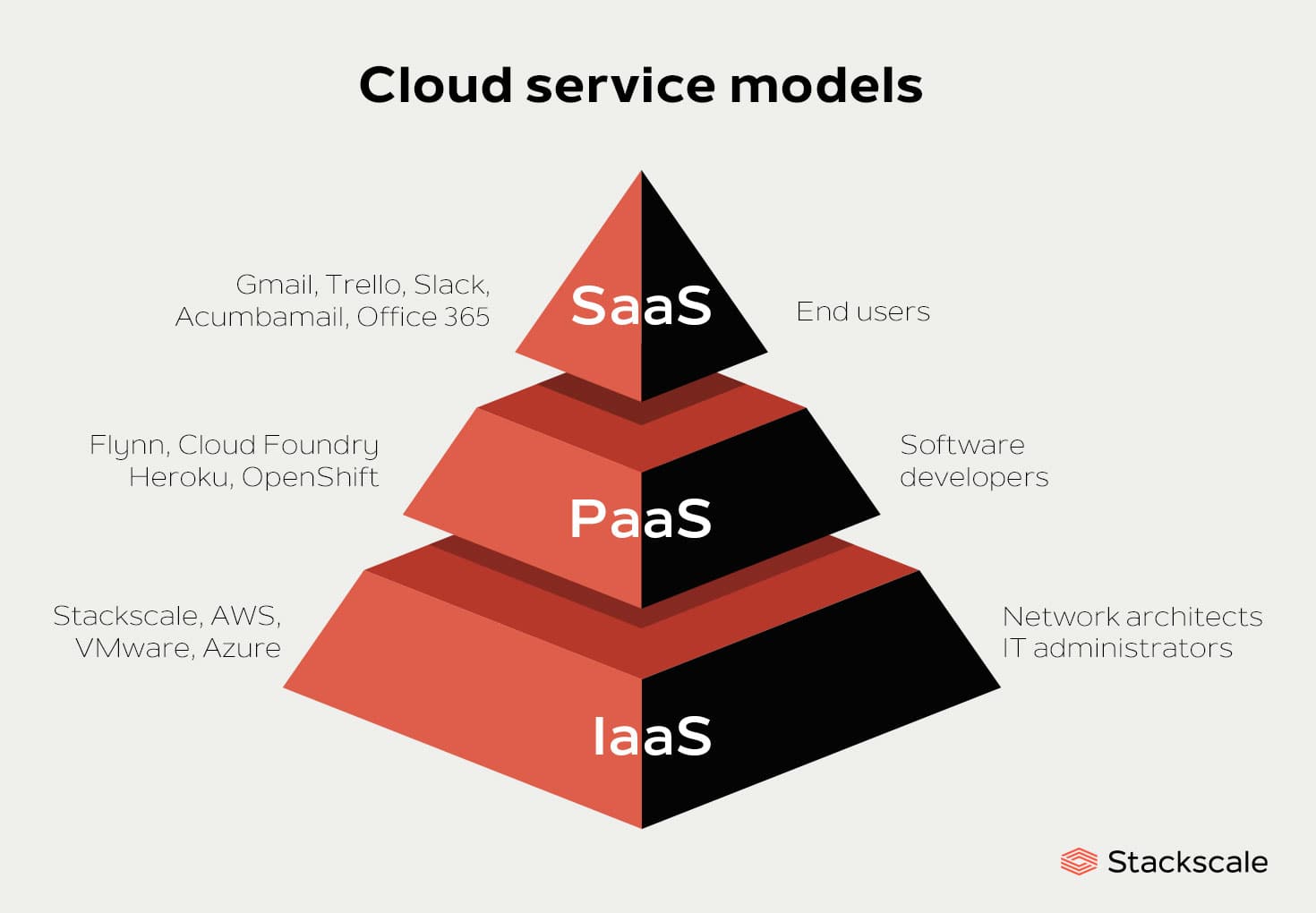
SaaS 🍕
Software as a service (or SaaS) is a service provided by Cloud providers delivering applications over the Internet. Instead of installing and maintaining software, you simply access it via the Internet.
Examples of such services are - Google G suite, Slack, Shopify etc.
My favorite Image is this 👇

A perspective of Cloud services is shown in a form of Pizza as a service model. ☝
Cloud deployment models 🕸
Public 🙋♂️
A public cloud is open to all to store and access information on the Internet. It makes resources such as applications and storage available to the general public.
Advantages of using the Public cloud:
Cheaper than Private and Hybrid
The public cloud is maintained by the cloud service provider, so you do not need to worry about maintenance.
Better flexibility and Integration
Private 🔐
An internal or corporate cloud is another name for a private cloud. Organizations use it to construct and operate their own data centers, either internally or through a third party. Opensource tools like Eucalyptus and OpenStack can be used to deploy it easily.
Advantages of the Private cloud:
Higher security
Better performance
Hybrid 🗝
Hybrid Cloud = Private cloud + Public cloud
Examples of Hybrid cloud: Google Application Suite (Gmail, Google Apps, and Google Drive), Office 365 (MS Office on the Web and One Drive), and Amazon Web Services.
Community 🤼
To share information between an organization and a particular community, a group of various organizations can access systems and services through a community cloud. One or more community-based organizations, a third party, or a combination of them own, manage and run it.
Conclusion 👋

Cloud has enabled people to work together more efficiently, regardless of their location. Collaborative tools like Google Docs, Dropbox, and Slack allow teams to share documents, files, and ideas in real-time, making it easier for them to work together on projects.
Cloud has made it more cost-effective for businesses to manage their IT infrastructure. Instead of investing in expensive hardware and software, businesses can use cloud-based solutions that are scalable and cost-effective
In simple terms, It's just someone providing their services on the internet to help us so that we focus on selling our product and let the cloud providers handle the complex stuff such as the infrastructure, platform etc.